
Flag of CARICOM; an alliance that includes almost all Caribbean States.
The Caribbean Spanish: Caribe; Dutch: Caraïben'; Caribbean Hindustani: कैरिबियन (Kairibiyana); French: Caraïbe or more commonly Antilles) is a region that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean), and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and
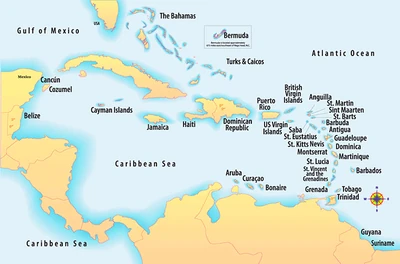
Location of the Caribbean
north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region comprises more than 700 islands, islets, reefs, and cays. These islands generally form island arcs that delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea. The Caribbean islands, consisting of the Greater Antilles on the north and the Lesser Antilles on the south and east (including the Leeward Antilles), are part of the somewhat larger West Indies grouping, which also includes the Lucayan Archipelago (comprising The Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands) north of the Greater Antilles and Caribbean Sea. In a wider sense, the mainland countries of Belize, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana are also included.
Geo-politically, the Caribbean islands are usually regarded as a sub-region of North America and are organized into 30 territories including sovereign states, overseas departments, and dependencies. From December 15, 1954, to October 10, 2010 there was a country known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five states, all of which were Dutch dependencies. While from January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962, there was also a short-lived country called the Federation of the West Indies composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies. The West Indies cricket team continues to represent many of those nations.
Definition[]
The word "Caribbean" has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political. The Caribbean can also be expanded to include territories with strong cultural and historical connections to slavery, European colonization, and the plantation system.
- The United Nations geoscheme for the Americas accords the Caribbean as a distinct region within The Americas.
- Physio-graphically, the Caribbean region is mainly a chain of islands surrounding the Caribbean Sea. To the north, the region is bordered by the Gulf of Mexico, the Straits of Florida, and the Northern Atlantic Ocean, which lies to the east and northeast. To the south lies the coastline of the continent of South America.
- Politically, the "Caribbean" may be centred on socio-economic groupings found in the region. For example, the bloc known as the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) contains the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, the Republic of Suriname in South America, and Belize in Central America as full members. Bermuda and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the Atlantic Ocean, are associate members of the Caribbean Community. The Commonwealth of the Bahamas is also in the Atlantic and is a full member of the Caribbean Community.
- Alternatively, the organisation called the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) consists of almost every nation in the surrounding regions that lie on the Caribbean, plus El Salvador, which lies solely on the Pacific Ocean. According to the ACS, the total population of its member states is 227 million people.
Geography, Geology and Climate[]
The geography and climate in the Caribbean region varies: Some islands in the region have relatively flat terrain of non-volcanic origin. These islands include Aruba (possessing only minor volcanic features), Barbados, Bonaire, the Cayman Islands, Saint Croix, the Bahamas, and Antigua. Others possess rugged towering mountain-ranges like the islands of Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, Dominica, Montserrat, Saba, Saint Kitts, Saint Lucia, Saint Thomas, Saint John, Tortola, Grenada, Saint Vincent, Guadeloupe, Martinique, and Trinidad & Tobago.
Cayo de Agua in Los Roques archipelago, Venezuela.
Definitions of the terms Greater Antilles and Lesser Antilles often vary. The Virgin Islands as part of the Puerto Rican bank are sometimes included with the Greater Antilles. The term Lesser Antilles is often used to define an island arc that includes Grenada but excludes Trinidad and Tobago and the Leeward Antilles.
The climate of the area is tropical but rainfall varies with elevation, size, and water currents (cool upwellings keep the ABC islands arid). Warm, moist tradewinds blow consistently from the east creating rainforest/semidesert divisions on mountainous islands. Occasional northwesterlies affect the northern islands in the winter. The region enjoys year-round sunshine, divided into 'dry' and 'wet' seasons, with the last six months of the year being wetter than the first half.
The waters of the Caribbean Sea host large, migratory schools of fish, turtles, and coral reef formations. The Puerto Rico trench, located on the fringe of the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea just to the north of the island of Puerto Rico, is the deepest point in all of the Atlantic Ocean.
Hurricanes that sometimes batter the region usually strike northwards of Grenada and to the west of Barbados. The principal hurricane belt arcs to northwest of the island of Barbados in the Eastern Caribbean.
The region sits in the line of several major shipping routes with the Panama Canal connecting the western Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean.
Island Groups[]
Greater Antilles[]
- Cuba
- Puerto Rico
- Jamaica
- Cayman Islands
Hispaniola[]
- Haiti
- Dominican Republic
Lesser Antilles[]
Leeward Islands[]
- US Virgin Islands
- British Virgin Islands (United Kingdom)
- Anguilla (United Kingdom)
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Saint Martin (France)
- Saint Maarten (Netherlands)
- Saba (Netherlands)
- Saint Estatius (Netherlands)
- Saint Barthélemy (France)
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Montserrat (United Kingdom)
- Guadeloupe (France)
Windward Islands[]
- Dominica
- Martinique (France)
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Grenada
- Barbados
- Trinidad and Tobago
Leeward Antilles (Dutch Antilles)[]
- Aruba (Netherlands)
- Curaçao (Netherlands
- Bonaire (Netherlands)